Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Recognizing Leg Pain Symptoms
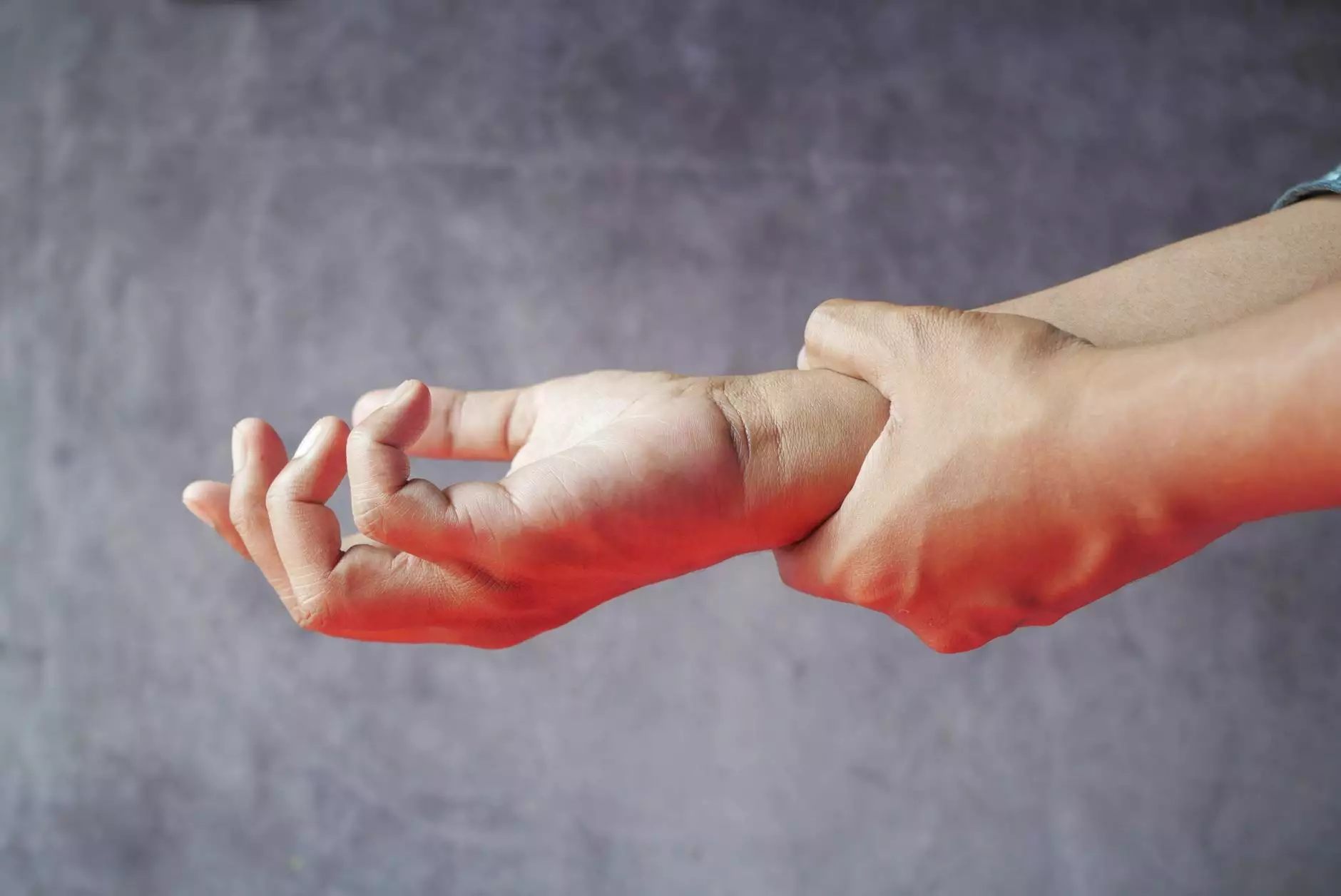

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, often in the legs. Recognizing the leg pain symptoms associated with DVT can be crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a part of a larger condition known as venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes both DVT and pulmonary embolism (PE). A thrombus (blood clot) forms in the deep veins, usually in the lower leg or thigh, leading to potential complications if not treated on time.
Common Symptoms of DVT
The symptoms of deep vein thrombosis can be subtle or quite pronounced, but there are key indicators that can alert individuals to the possibility of this condition. Here are the most common leg pain symptoms associated with DVT:
- Swelling in One Leg: The affected leg may swell up significantly compared to the other leg. This is one of the hallmark signs of DVT.
- Pain or Tenderness: Patients often experience pain or tenderness in the affected leg, typically starting in the calf. This pain may feel like cramping or soreness.
- Red or Discolored Skin: The skin over the area of the clot may appear reddened or discolored. It can also feel warm to the touch.
- Enlarged Veins: Superficial veins near the surface of the skin may become more visible or engorged, making the leg appear differently shaped.
- Increased Warmth: The area around the clot may feel warmer than surrounding tissues, indicating inflammation.
Risk Factors for Developing DVT
Understanding the risk factors associated with DVT can help individuals identify their susceptibility and take preventive measures. Here are some major risk factors:
- Prolonged Immobility: Long periods of sitting or inactivity, such as during long flights or car rides, can slow down blood flow and lead to clots.
- Recent Surgery or Injury: Surgical procedures, particularly orthopedic surgeries, and serious injuries can increase the risk of clot formation.
- Age: Individuals over 60 are at greater risk of DVT, though younger individuals can also be affected.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional pressure on veins in the legs, increasing the likelihood of clot formation.
- Hormonal Factors: Certain medications, including birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy, can increase clotting tendencies.
- Family History: A personal or family history of DVT can raise the chances of developing the condition.
Understanding the Severity of Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT is not only concerning because of its symptoms; it also poses serious health risks. If a blood clot breaks loose, it can travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism, which is potentially life-threatening.
Recognizing Complications: Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a piece of the clot travels to the lungs and obstructs a blood vessel there. Symptoms of PE may include:
- Shortness of Breath: Sudden difficulty in breathing can signal an emergency situation.
- Chest Pain: Sharp or stabbing pain, especially when breathing deeply.
- Coughing Up Blood: This is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention.
- Rapid Heart Rate: An increased heart rate can be a sign that your body is under stress.
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis
If you suspect you may have DVT, seeking prompt medical care is vital. A healthcare provider will review your symptoms and medical history, perform a physical examination, and may employ several diagnostic tests, including:
- Ultrasound: This is the most common test for diagnosing DVT, providing visual evidence of clot formation.
- D-dimer Test: A blood test that measures the presence of a clot: elevated levels may indicate DVT.
- Venography: An older but definitive test where a contrast dye is injected into a vein, allowing for X-ray imaging of veins.
Treatment Options for DVT
Upon diagnosis, treatment focuses on preventing the clot from enlarging and reducing the risk of PE. Common treatment strategies include:
- Anticoagulants: Commonly referred to as "blood thinners," these medications reduce the ability of blood to clot. Examples include warfarin and newer oral anticoagulants like rivaroxaban.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help reduce swelling and pain while improving blood circulation in the legs.
- Thrombolytics: In severe cases, clot-busting medications may be used to dissolve clots more rapidly.
- Inferior Vena Cava Filter: In certain situations, this filter is placed in the inferior vena cava to prevent clots from traveling to the lungs.
Preventive Measures to Avoid DVT
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are significant steps individuals can take to lower their risk of developing DVT:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity enhances circulation and prevents blood from pooling in the legs.
- Leg Exercises: During long periods of sitting or traveling, perform simple leg exercises, such as ankle pumps or calf raises.
- Hydrate: Keeping well-hydrated is essential, particularly during travel, as dehydration can increase the risk of clot formation.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Wearing loose, comfortable clothes helps improve blood flow in the legs.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Those with risk factors should have regular health screenings and discussions about their level of risk.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any symptoms of deep vein thrombosis, especially swelling in one leg, pain or tenderness, or any of the warning signs of pulmonary embolism, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional immediately. Timely intervention can save lives and prevent severe complications.
Conclusion
In summary, deep vein thrombosis is a serious medical condition with various leg pain symptoms and potential complications. Being aware of the risk factors, recognizing the signs, seeking quick diagnosis, and understanding treatment options are essential in managing and preventing DVT. For tailored advice on prevention and treatment, individuals are encouraged to consult healthcare providers, like those at Truffles Vein Specialists, who specialize in vascular health.
Staying informed and proactive about your vascular health can significantly reduce your risk of DVT and related complications.
deep vein thrombosis leg pain symptoms